As the public environmental awareness and the media’s interest in sustainability and natural resources exploitation increases, crucial global issues get a higher visibility. For instance, we hear about the ecological footprint more and more often. But what is it? What’s its purpose? And how is it calculated?
What is it?
The ecological footprint is an indicator that measures the amount of natural surface area that is needed in order to restore the resources we consume and to absorb the waste we produce. It’s expressed in global hectares, and it tracks the use of six categories of productive surface areas:
- cropland;
- grazing land;
- fishing grounds;
- built-up land;
- forest area;
- carbon demand on land.
This indicator is essential to measure the portion of environment needed to produce the goods and services demanded by a population, as well as to absorb its waste. The food we eat, the goods and products we buy, the junk we produce… it all contributes to determining our ecological footprint, and therefore the pressure we exert on our planet.
What is its purpose?
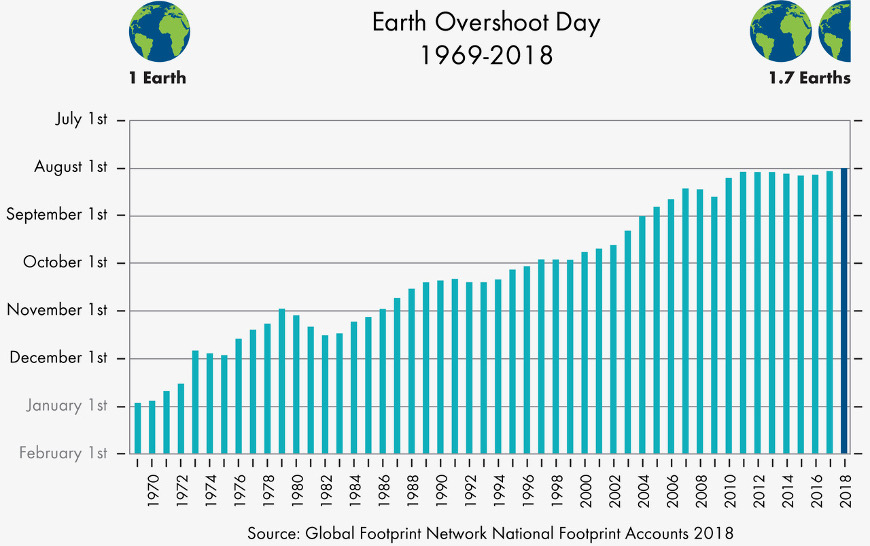
To discuss the ecological footprint, we must refer to the Global Footprint Network, an international non-profit organization committed to promoting a more sustainable way of life. Every year, this organization discloses the Earth Overshoot Day, which marks the date in which humanity exhausts all the natural resources that Earth is able to generate throughout the whole year. In simple terms, when we exceed nature’s annual budget. It is precisely to calculate the Earth Overshoot Day (in 2020, it was August 22) that the Global Footprint Network implemented the idea of the ecological footprint.
When was it introduced?
British Columbia University professor William Rees first mentioned this term, together with his then student Mathis Wackernagel, founder and current president of the Global Footprint Network (sounds familiar?). In 1996, they published a book titled Our Ecological Footprint: Reducing Human Impact on the Earth, in which they introduced this new notion.
How is it calculated?
Each country’s footprint is calculated by the Global Footprint Network and then compared with global biocapacity, to determine the Earth Overshoot Day.
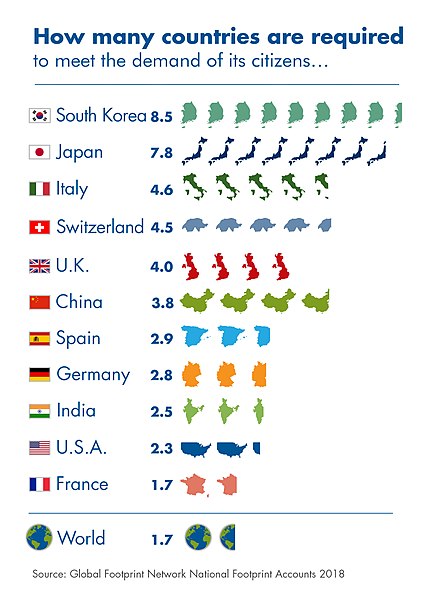

The association also made available an online calculator, for everyone to calculate their own ecological footprint and Earth Overshoot Day.
How many planets would we need if everyone lived like you? Let us know with a comment!
Cover image: photo by Colin Behrens on Pixabay.




